|
U sing
Telnet requires client software which acts as a terminal emulator.
We highly recommend CRT for Telnet use to all of our clients.
CRT is a 32-bit terminal
emulator designed for Internet and intranet use with support for
both the telnet and rlogin protocols. CRT includes a 30-day,
try-before-you-buy, fully-functional evaluation license. CRT is
extremely customizable and easy to use. Remote sites can be easily
accessed by just entering a hostname.
CRT is packed with features. Some of the more popular features
include named sessions, auto login, printing, zmodem file transfer,
emacs mode, and SOCKS firewall support.
CRT has received many awards, including 5 cows from Tucows
among many others. CRT is manufactured by Van
Dyke Technologies.
An alternative to CRT is Windows Telnet, which comes free with
Windows 95/98. Windows Telnet is a very basic Telnet application
with no additional features.
Before proceeding, please be sure you
have downloaded and installed any version of CRT 2.x.
First, open CRT from Windows. Once you have opened CRT (perhaps you
had to agree to a license
agreement or acknowledge an evaluation period), you should see a
screen like the one shown below.
Once you see
the screen displayed above click the "New" button.
Next, you should see a screen
like the one shown below. Complete the blank fields with your name
and hostname.
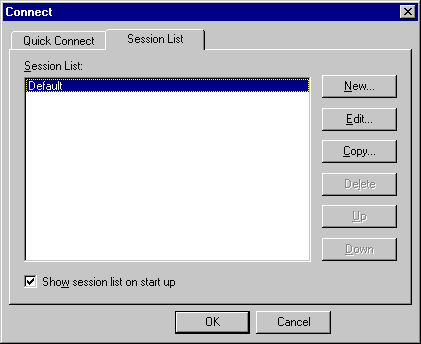
Save the configuration on
the screen by pressing "OK". Your screen should now look
like the screen below with your Session List.
Press the "OK" button to log into Telnet. You will be
prompted for your login ( ) and password (use your system password).
Once you login to your account you can begin issuing commands from
Telnet.
You will automatically be logged into the "root" of your
account. The root of your account will be displayed as
"/". Below is the dialogue you should see when you log
into your virtual server via Telnet:
SunOS 5.7
login:
Password:
Sun Microsystems Inc. SunOS 5.7 Generic May 1999
****************************************************************
*
*
* Welcome to the CTSH shell v 2.0!
*
* Today is: September 18, 1999 at 3:26:24 PM
*
*
* You are currently using MB of disk space.
* You have transferred MB of bandwidth.
*
* Anonymous FTP is Enabled
*
*
****************************************************************
You currently have X POP3 E-Mail accounts.
Your POP3 E-Mail accounts status:
= You have new mail.
Welcome to ! All activity is monitored at all times. Please
observe and obey the following rules:
1. IRC bots of any type are strictly forbidden.
2. Any programs which run in the background are forbidden.
3. The use of external FTP and webservers are strictly forbidden.
4. Excessive use of crontab is forbidden.
5. The gcc compiler may be used only for CGI programs relating to your website.
Anyone found in violation of these rules are subject to all Telnet privileges
being revoked without notice.
To see this message again at anytime enter: stats
:/ >
From here, you can begin issuing commands from Telnet.
Telnet is very powerful in the sense
that you can edit your files directly through a terminal emulator,
which avoids any need to perform file transfers from your client to
your virtual server. Below are some common Telnet commands.
pico <filename> -- Pico is a common text editor used to modify
files.
cd <directory> -- cd, or change directory, is a binary which
allows you to move into different directories of your virtual
server. Very essential!
ls -- ls is a commonly used binary which lists all files and
directories in the current working directory.
pine -- pine is a popular mail utility that allows you to check and
send e-mail directly from your virtual server.
Congratulations.
You have completed this short tutorial on telnet.
|